In today’s digital age, cybersecurity is no longer just a technical concern—it’s a fundamental necessity for individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. As we become increasingly dependent on technology, Cybercrime’s risk grows in frequency and sophistication. Hackers are employing advanced tactics, from ransomware and phishing schemes to AI-driven cyber threats, making cybersecurity a critical issue that affects everyone.
The financial and operational impact of cybercrime is staggering. Businesses suffer from data breaches, operational downtime, and reputational damage, while individuals face identity theft and financial fraud. Governments, too, are under constant threat, with cyberattacks targeting national security, infrastructure, and sensitive information. The rising costs associated with these threats highlight the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Would You Rather Listen To Our Podcast
1. The Escalating Cost of Cybercrime
Cybercrime’s Global Financial Toll
The financial burden of cybercrime is growing at an alarming rate. In 2015, cybercrime inflicted $3 trillion in global damages, but by 2025, that number is expected to skyrocket to $10.5 trillion annually. If that trend continues, some projections estimate that by 2027, the total cost could reach $24 trillion, making cybercrime one of the most economically damaging threats in the modern world.
The Rising Cost of Ransomware
Ransomware—where attackers encrypt a victim’s data and demand payment for its release—has become one of the most financially devastating forms of cybercrime.
- By 2031, ransomware damages are projected to hit $265 billion per year, a dramatic increase from $42 billion in 2024.
- The cost of recovering from ransomware attacks is also on the rise. In 2024, organizations spent an average of $2.73 million per attack, nearly $1 million more than in 2023.
With cybercriminals continuously refining their tactics and expanding their targets, the economic impact of cybercrime is set to grow exponentially, making cybersecurity investments more crucial than ever.

2. The Growing Number of Cybercrime and Security Vulnerabilities
The digital landscape is becoming increasingly complex, and with it, the number of security vulnerabilities continues to rise. Cybercriminals exploit these weaknesses to infiltrate systems, steal data, and launch attacks. The surge in reported Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) is a clear indicator of the growing cybersecurity challenge:
- By mid-2024, 22,254 CVEs had already been reported—marking a 30% increase from 2023 and a 56% jump from 2022.
- Over 30,000 new vulnerabilities were disclosed in the past year alone, representing a 17% year-over-year increase.
As new software and digital services emerge, the attack surface for cybercriminals expands. Security researchers are identifying vulnerabilities faster than ever, but the sheer volume of threats makes it difficult for organizations to keep up with patching and defense measures. The increasing complexity of cyber threats, combined with the rapid disclosure of vulnerabilities, underscores the need for proactive cybersecurity strategies.
3. Why Cybercrime is Increasing
The rise in cybercrime isn’t random—it’s fueled by a combination of technological advancements and systemic weaknesses that make cyberattacks easier and more profitable than ever before.
1. Global Connectivity & Cloud Reliance → Greater Data Exposure
With more businesses and individuals relying on cloud storage and digital services, vast amounts of sensitive data are exposed to potential breaches. The convenience of remote access and cloud computing comes with an increased risk of cybercriminals exploiting misconfigured security settings and stolen credentials.
2. Sophistication of Cybercriminals → Advanced Social Engineering, Ransomware & Phishing
Hackers are constantly refining their tactics, using AI-driven phishing campaigns, deepfake technology, and ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) to increase their success rates. Social engineering remains one of the most effective attack methods, tricking users into revealing credentials or downloading malicious software.
3. Internet’s Decentralized Structure → Difficult to Police Cross-Border Cybercrime
The global nature of the internet allows cybercriminals to operate beyond the reach of law enforcement. Attackers can target victims in different countries while remaining outside the jurisdiction of local authorities, making prosecution nearly impossible in many cases.
4. The Dark Web Economy → A Profitable Marketplace for Stolen Data & Hacking Tools
The dark web has become a thriving black market for cybercrime, where hackers buy and sell stolen financial data, login credentials, and exploit kits. With cybercrime now a multi-billion-dollar industry, even amateur hackers can purchase ready-made attack tools, making cyberattacks more accessible and widespread.
5. Growth of IoT & Mobile Devices → Expanding Attack Surface
As more Internet of Things (IoT) devices and mobile gadgets connect to the Internet, the number of entry points for cybercriminals increases. Many IoT devices have weak security or lack regular software updates, making them easy targets for hackers looking to infiltrate networks.
Cybercrime is evolving rapidly, fueled by technological advancements and an expanding digital ecosystem. Without proactive security measures, individuals and organizations will remain vulnerable to this growing and costly threat.

4. The Importance of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is no longer optional—it is a critical necessity for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. As cyber threats become more frequent and severe, the consequences of inadequate protection can be devastating.
Cybercrime Protection Against Data Theft & Breaches
Sensitive information, including personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), intellectual property, and financial records, is highly valuable to cybercriminals. A single data breach can expose millions of records, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and corporate espionage. Organizations that fail to secure their data not only suffer financial losses but also face severe reputational damage and legal consequences.
National Security Risks from Cyberattacks
Governments and industries are prime targets for cyberattacks that threaten national security. Cybercriminals and state-sponsored hackers exploit vulnerabilities to infiltrate critical infrastructure, disrupt essential services, and steal classified information. Attacks on power grids, financial institutions, and communication networks can have far-reaching consequences, including economic instability and geopolitical tensions.
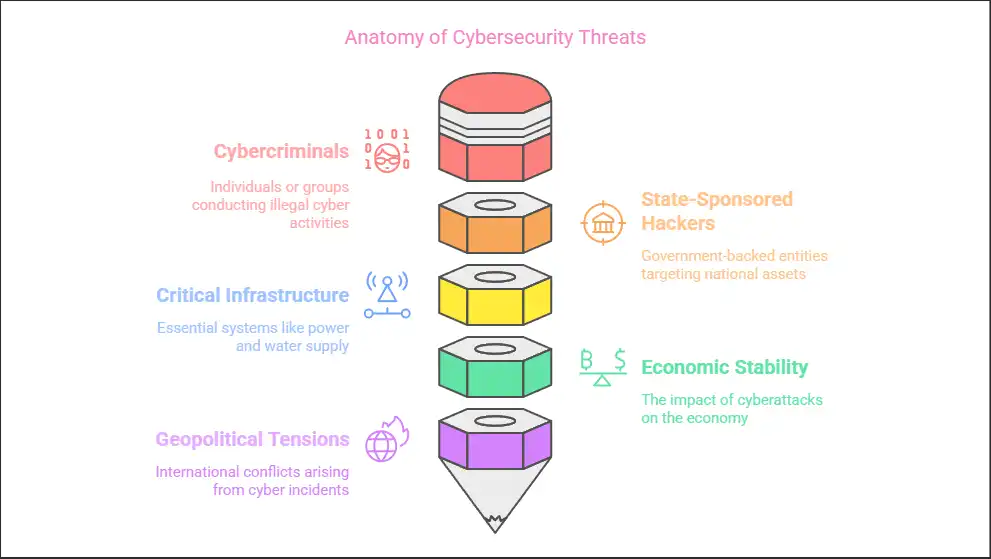
The Need for Proactive Cybersecurity Measures
Reactive approaches are no longer enough. Organizations must implement proactive security measures such as:
- Continuous threat monitoring to detect and mitigate attacks before they cause damage.
- Regular security updates and vulnerability patching to close potential entry points for hackers.
- Employee training programs to reduce the risks associated with phishing and social engineering attacks.
Cybersecurity is an ongoing battle, requiring constant adaptation to evolving threats. Businesses, governments, and individuals must prioritize robust security strategies to safeguard sensitive information and ensure digital resilience.
5. The Role of AI in Cybercrime
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the cybersecurity landscape, offering both powerful defensive tools and new risks as cybercriminals weaponize AI for sophisticated attacks.
AI-Driven Defenses → Continuously Evolving to Counter Sophisticated Attacks
AI-powered cybersecurity solutions can:
- Analyze vast amounts of data in real-time to detect and prevent threats.
- Identify patterns and anomalies that indicate potential cyberattacks.
- Automate incident response, reducing the time it takes to neutralize threats.
By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI can continuously adapt to emerging attack patterns, making security systems more resilient against evolving cyber threats.
AI-Powered Cyberattacks → More Realistic Phishing & Automated Exploits
While AI enhances cybersecurity, it also empowers cybercriminals. Attackers are now using AI to:
- Generate highly convincing phishing emails that mimic human communication.
- Automate the discovery and exploitation of software vulnerabilities.
- Create deepfake technology to deceive individuals and manipulate information.
This AI arms race between defenders and attackers highlights the urgent need for organizations to invest in cutting-edge security solutions.

The Need for a Hybrid Approach → Combining AI with Human Expertise
While AI can detect and prevent many cyber threats, human expertise remains irreplaceable. Cybersecurity professionals play a crucial role in:
- Investigating complex threats that AI may not fully understand.
- Developing strategic security policies and best practices.
- Ensuring ethical and responsible use of AI in cybersecurity.
A hybrid approach, integrating AI-driven automation with human intelligence, is the key to maintaining strong cybersecurity defenses in an increasingly hostile digital landscape.
6. The Human Element in Cybercrime
Despite advancements in AI-driven security solutions, human expertise remains irreplaceable in the fight against cybercrime. Technology alone cannot counteract all threats—human intelligence, awareness, and strategic decision-making are essential components of a robust cybersecurity strategy.
Human Expertise Remains Critical
AI can analyze data, detect anomalies, and automate responses, but it lacks the contextual understanding, intuition, and adaptability that human experts provide. Cybercriminals constantly develop new attack strategies that AI may not immediately recognize, making human intervention necessary for:
- Interpreting complex threats beyond AI’s current detection capabilities.
- Developing security policies tailored to specific organizations and industries.
- Investigating breaches and responding to sophisticated attacks where AI-generated alerts may not provide sufficient context.
Cybercrime Security Awareness & Education
One of the biggest cybersecurity risks is human error—many cyberattacks succeed due to weak passwords, phishing scams, or inadvertent data leaks. Organizations must prioritize:
- Employee cybersecurity training to recognize and avoid phishing and social engineering attacks.
- Strict access control policies to limit exposure to sensitive information.
- Regular security drills and awareness programs to reinforce best practices.
An informed and security-conscious workforce is a company’s first line of defense against cyber threats.
Hybrid Security Approach → AI + Human Intervention
The most effective cybersecurity strategies combine AI’s speed and efficiency with human expertise. This hybrid approach ensures:
- Faster threat detection and mitigation using AI-driven automation.
- More accurate risk assessments with human oversight.
- Improved adaptability to emerging threats by integrating machine learning with human intelligence.
By blending AI-powered tools with human decision-making, organizations can create a more resilient cybersecurity framework capable of handling both known and unknown threats.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity has become one of the biggest challenges of the digital era, affecting individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. With rising cybercrime costs, an increasing number of vulnerabilities, and more sophisticated cyber threats, organizations can no longer afford to be complacent.
To stay protected, investing in cybersecurity is essential. This includes:
- Implementing AI-driven security solutions to detect and prevent threats.
- Prioritizing human expertise and cybersecurity awareness to reduce risks.
- Adopting a proactive approach with continuous monitoring, updates, and security best practices.
Call to Action
Cyber threats are evolving faster than ever, making cybersecurity everyone’s responsibility. Both organizations and individuals must:
- Stay vigilant against potential threats.
- Educate themselves on cybersecurity best practices ( Like using a VPN ).
- Invest in strong security measures to protect data, privacy, and digital assets.
The digital world is only getting more complex—being proactive today means staying secure tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why is cybersecurity a major concern today?
Cybersecurity is a critical issue because cyberattacks are becoming more frequent and sophisticated. The rise of ransomware, phishing scams, and data breaches puts individuals, businesses, and even governments at risk, leading to financial losses and privacy violations.
2. How much does cybercrime cost the global economy?
The financial impact of cybercrime is staggering. By 2025, it is projected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually, and by 2027, that number could reach $24 trillion. The cost of recovering from cyberattacks, especially ransomware, continues to rise as well.
3. What are the biggest cybersecurity threats right now?
Some of the top cybersecurity threats include ransomware attacks, phishing scams, malware infections, data breaches, and social engineering tactics. The increasing number of vulnerabilities in software and IoT devices also makes cybercrime easier to execute.
4. How can businesses protect themselves from cyberattacks?
Businesses can improve their cybersecurity by implementing strong password policies, using multi-factor authentication, conducting regular security audits, training employees on cybersecurity best practices, and investing in AI-powered security solutions.
5. Will AI replace human cybersecurity experts?
AI plays a crucial role in cybersecurity, but it cannot replace human expertise. While AI can detect threats and automate security responses, human cybersecurity professionals are still needed to analyze complex threats, make strategic decisions, and adapt to new attack methods. A hybrid approach combining AI and human intelligence is the most effective defense strategy.

